...Because You Didn’t Hire Enough Humanities Graduates...
Critical and contextual thinking are the new superpowers!
Walk the halls of any failing organization in 2030 and you will see the same patterns: brilliant engineers with no sense of context; marketing departments drowning in dashboards, but blind to meaning; and leaders who can’t connect decisions to human experience.
The tragedy isn’t lack of intelligence...but lack of perspective.
For years, executives doubled down on “hard skills.” They thought: “Hire more coders. Scale the analysts. Push productivity through process.” And yet, here we are: disengaged employees, customers who don’t feel understood or valued, and cultures that suffocate innovation.
What organizations (and their leaders) missed is that human beings drive business, not algorithms or workflows. And human beings are messy, contradictory, and infinitely complex. To make sense of that complexity requires something more than efficiency metrics. It requires context, empathy, narrative, and the ability to hold multiple truths at once.
“Complex problems need people who are energized by tackling big, complex challenges.”
This is precisely what the Humanities teach. Graduates who have wrestled with history, philosophy, literature, creative writing, or art bring more than cultural awareness. They bring tools for thinking systemically, questioning assumptions, and connecting disparate dots. They can spot patterns across centuries, frame ethical dilemmas in ways that unlock better strategy, and articulate meaning when others only see noise.
The Authentic Leader argues that leadership is ultimately about one question: Are we helping people? Leaders who can’t answer that—who can’t even see it—build organizations that crumble when faced with complexity. Humanities graduates, by training, are equipped to keep asking that question, even when the numbers look good on the quarterly report.
This is not an argument against technology, finance, or engineering talent. Rather, it is a call for balance. If you want to future-proof your business, you need people who can code and people who can contextualize. People who can design systems and people who can challenge their consequences. Professionals who can solve problems and people who can imagine futures worth solving for.
Ignore this at your peril.
The companies that thrive in 2030 won’t be those with the most data. Instead, think of a future in which leaders and teams know what the data means for human lives. Complex problems need people who are energized by tackling big, complex challenges.
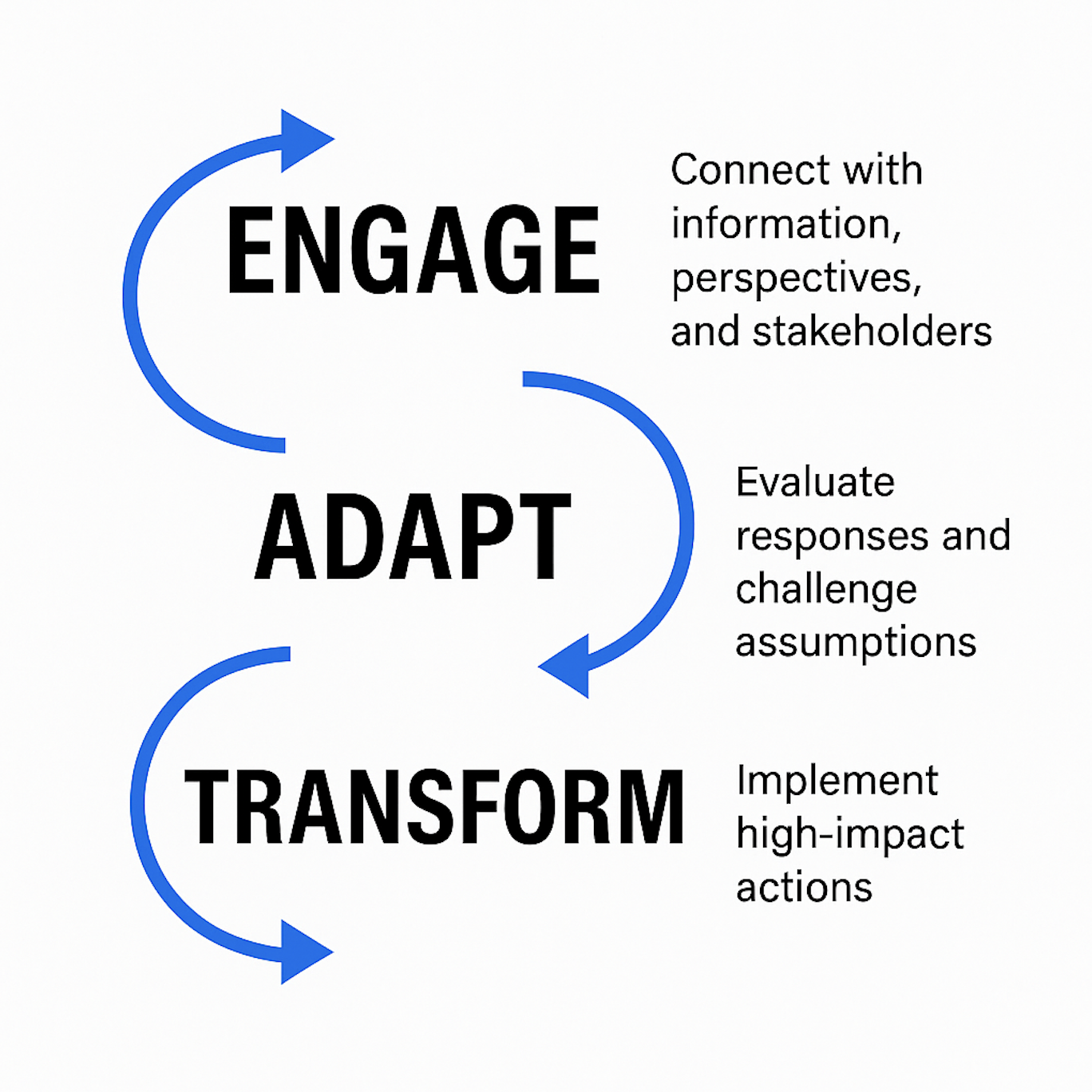
The EAT Model created by Bob Batchelor
Bob Batchelor is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Communication, Media, & Culture at Coastal Carolina University. He is a critically-acclaimed, bestselling cultural historian and biographer. He has published widely on American cultural history and literature, including Stan Lee: A Life and books on The Doors, Bob Dylan, The Great Gatsby, Mad Men, and John Updike. Batchelor earned his doctorate in English Literature from the University of South Florida.